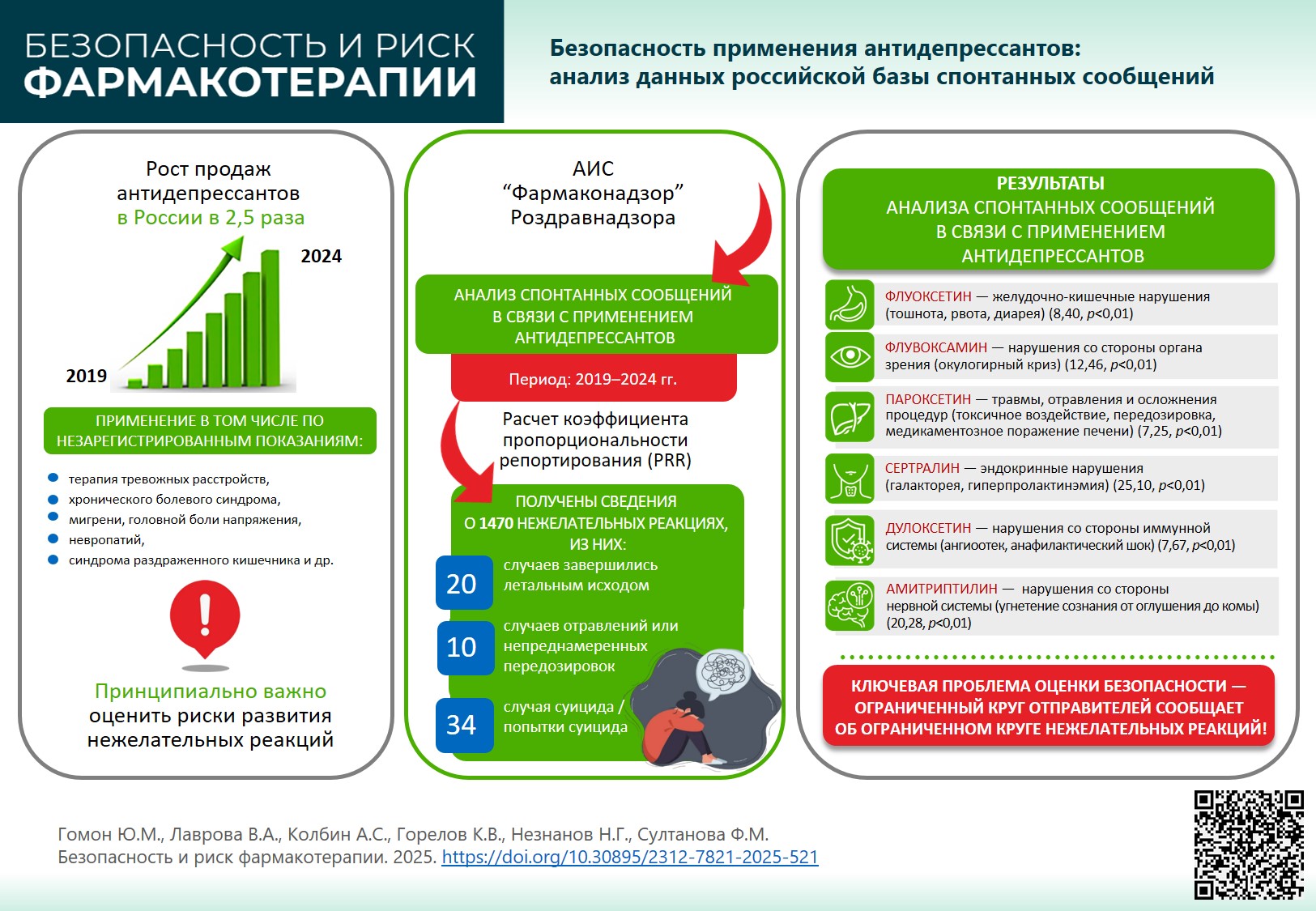
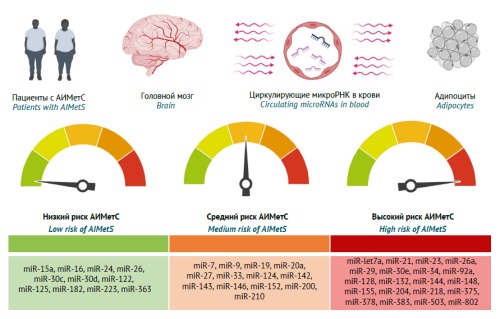
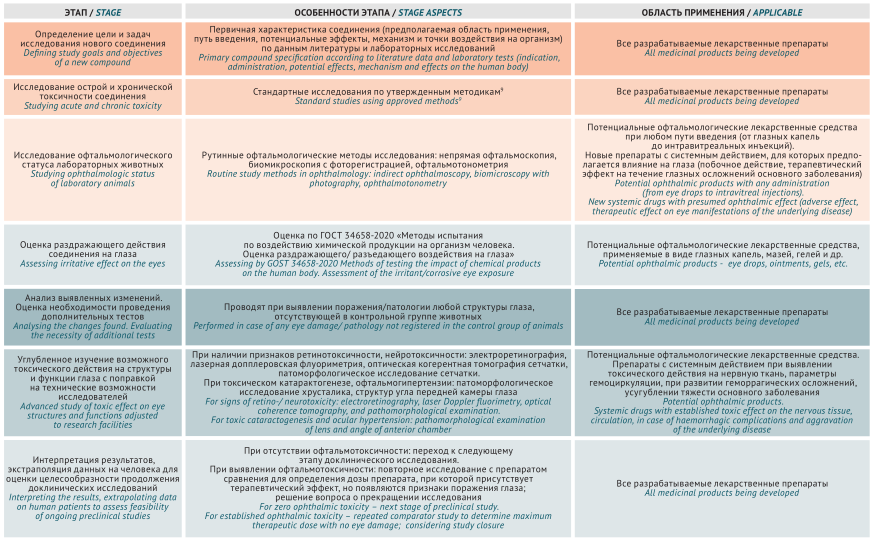
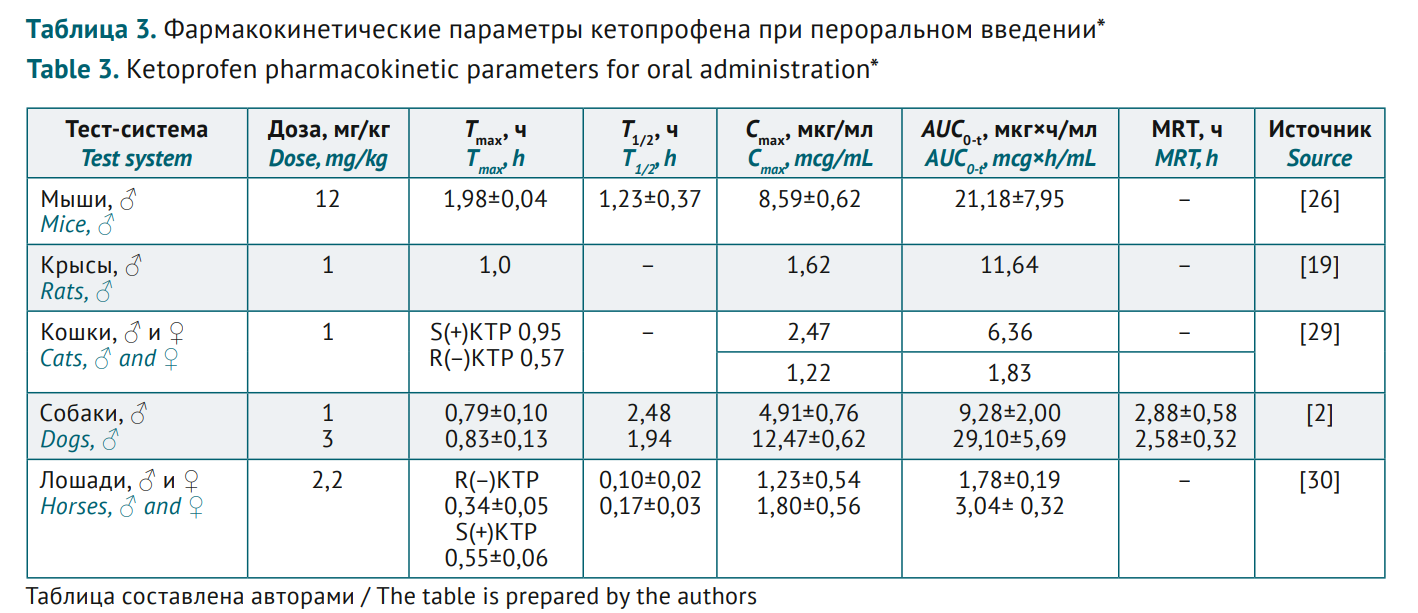
MAIN INFORMATION ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy is an open-access peer-reviewed scientific and applied research journal published both in print and online. It is the only Russian scientific journal covering safety and risks of pharmacotherapy in Russia. Founded in 1994.
Aim: to report on scientific achievements and practical experience in drug safety assurance and pharmacotherapy risk reduction.
Target audience: healthcare practitioners; clinical pharmacologists and other medical specialists; pharmacists; pharmacovigilance officers and managers in pharmaceutical companies; employees of expert bodies, preclinical and clinical trial centres, regulatory and supervisory bodies, and research institutes; lecturers and students of medical and pharmaceutical universities. For more information, see Aims and Scope section.
Publication frequency: quarterly (four issues per year).
Impact factor: the journal’s two-year RISC impact factor is 0,826 (2024).
Geographical diversity of the Editorial Board:
- three (3) continents,
- ten (10) countries,
- 17 cities
Peer-review procedure:
- double-blind peer review,
- a minimum of two (2) reviewers per manuscript
Key metrics:
- fourteen (14) days from submission to the first approval (on average),
- 151 days from submission to online publication (on average),
- 23% of invited authors,
- 63% of manuscripts accepted,
- 37,000 PDF uploads in 2023
Publication fee: free of charge.
Indexing: The journal is in the Scopus database (Accepted Titles May 2025), List of State Commission for Academic Degrees and Titles of Russian Ministry of Education and Science (K1 Category), Russian Science Citation Index, Russian Index of Science Citation, and DOAJ Seal. For more information on notation in other Russian and international databases, see Indexing section.
Registration: The journal is registered as a mass medium by the Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technologies and Mass Communications. Certificate PI No. FS77-82932 dated 14 March 2022.
Subscription index in the Press of Russia (Pressa Rossii) catalogue and in the Ural-Press agency – 57941.
Current issue
MAIN TOPIC: THE SUBTLE ART OF SOUL HEALING: QUO VADIS?
PRECLINICAL STUDIES
CLINICAL STUDIES
Announcements
2025-12-05
The Global Smart Pharmacovigilance Strategy published on the WHO website
World Health Organization has published The global smart pharmacovigilance strategy. The new strategy is a framework to develop and enhance the national safety monitoring systems, considering varying health care levels.
| More Announcements... |