MAIN TOPIC: THE SUBTLE ART OF SOUL HEALING: QUO VADIS?
Modern psychopharmacological research complements traditional monoamine theories by adopting new data on the role of neuroinflammation, the microbiome, and impaired neuroplasticity in the development of mental disorders. An insider perspective (an interview with a practicing specialist) is essential for assessing the real risks and prospects at an expert level, as well as understanding the complex ethical, medical, and social challenges associated with the development of new psychotropic medications. Renad N. Alyautdin, Dr. Sci. (Med.), Editor-in-Chief, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, Department for Medicine Safety Evaluation, Scientific Centre for Expert Evaluation of Medicinal Products, and Marina A. Kinkulkina, Dr. Sci. (Med.), Corresponding Member of RAS, Head of the Department of Psychiatry and Narcology, I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University, discussed the search for new therapeutic targets, the challenges of developing and implementing innovative drugs, and the options for minimising treatment risks for personalised medicine within the context of mental health treatment in the era of evolving psychopharmacotherapy.
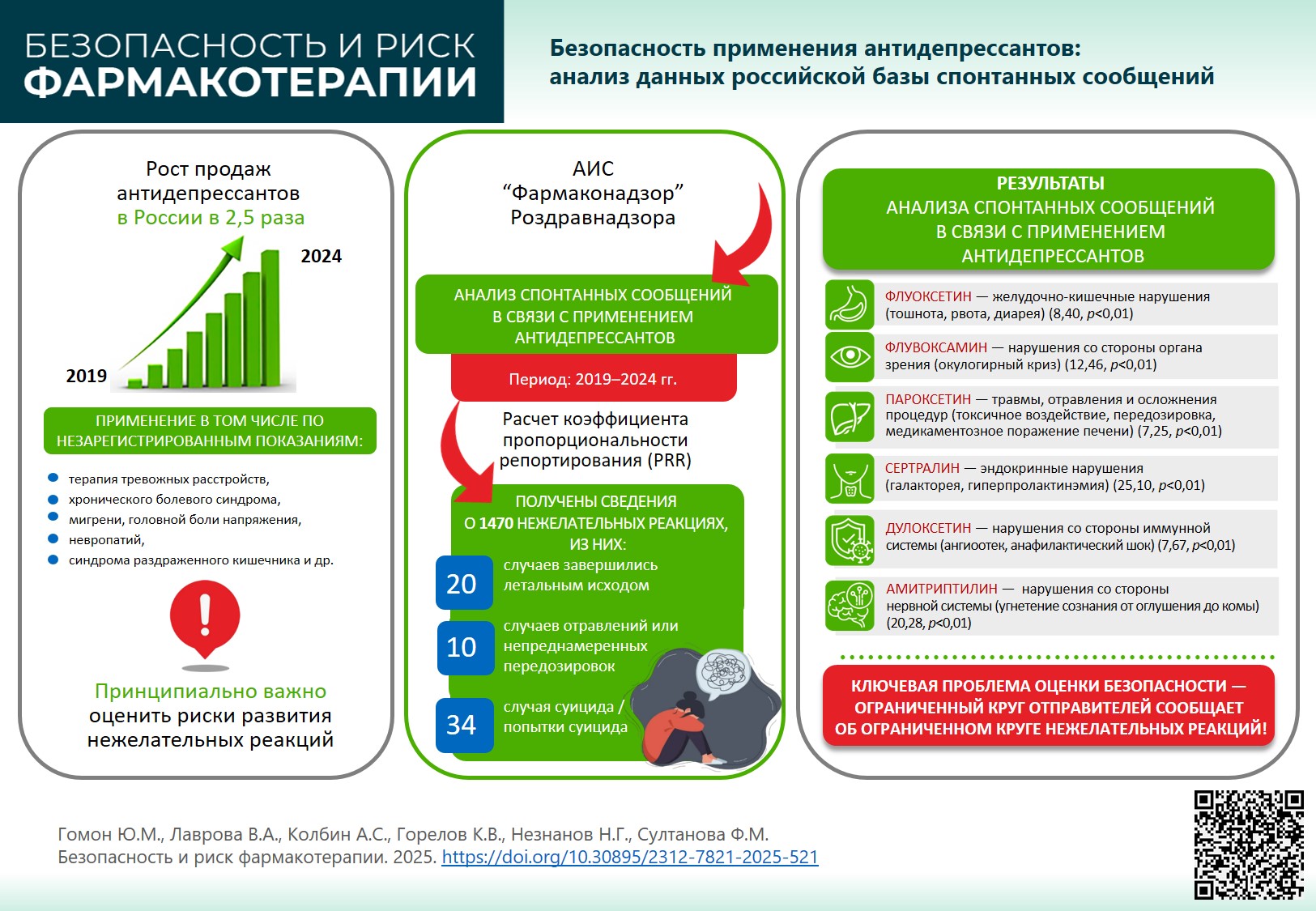
INTRODUCTION. Extensive use of antidepressants in a wide range of indications, including off-label use, as well as application in vulnerable groups of patients, shows the need to summarise the available safety data of these medicinal products.
AIM. This study aimed to evaluate safety profile of antidepressants prescribed for neurotic disorders in the Russian Federation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. The study analysed spontaneous reports registered by Pharmacovigilance database of Roszdravnadzor Automated Information System in 2019–2024 for medicines with international nonproprietary names: fluvoxamine, citalopram/escitalopram, paroxetine, fluoxetine, sertraline, venlafaxine, duloxetine, vortioxetine, amitriptyline, clomipramine, mirtazapine, and imipramine. Reporting odds ratio and proportional reporting ratio was calculated for each international non-proprietary name with respect to statistically significant disproportionality.
RESULTS. Amitriptyline resulted in the maximum number of reports (n=470), the minimum registered for imipramine (n=2). For most of the medicines, the total spontaneous reports over the five years of follow-up did not exceed 100. Statistically significant associations between the treatment and adverse drug reactions (ADRs) were demonstrated for the atypical antidepressant vortioxetine, for example, mental, endocrine, cardiac, and reproductive system disorders. Association with laboratory and instrumental disorders was confirmed for agomelatine. Among selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, the following ADR relationships were statistically significant: fluoxetine — gastrointestinal disorders; fluvoxamine — eye disorders; paroxetine — ADRs in the systemic organ class Injury, Poisoning and Procedural Complications; sertraline — endocrine disorders. Use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors venlafaxine and duloxetine was significantly associated with immune system disorders. Treatment with tricyclic antidepressant amitriptyline is associated with nervous system disorders. Moreover, there was a high reporting rate from singular health facilities and pharmaceutical companies regarding certain products (atypical antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors) and ADRs (such as oculogyric spasm for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors).
CONCLUSIONS. In 2019–2024, the number of spontaneous reports on ADRs caused by antidepressants increased every year; however, overall reporting remained low. Low number of spontaneous reports that do not align with actual consumption data, as well as discrepancy defined between incoming spontaneous reports on certain medicinal products and ADRs make it impossible to assess safety profile of the products considered. To determine safety profile of the medicinal products, further studies based on real clinical practice are recommended.
INTRODUCTION. Despite the proven clozapine effectiveness in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia, its use can cause adverse drug reactions, including clozapine-induced sialorrhea (CIS). Data on CIS pathogenesis are limited. Identifying CIS pharmacogenetic predictors will make it possible to both predict adverse drug reactions prior to therapy and specify individual pathogenetic elements.
AIM. This review aimed to identify CIS predictors using systematic analysis of literature data.
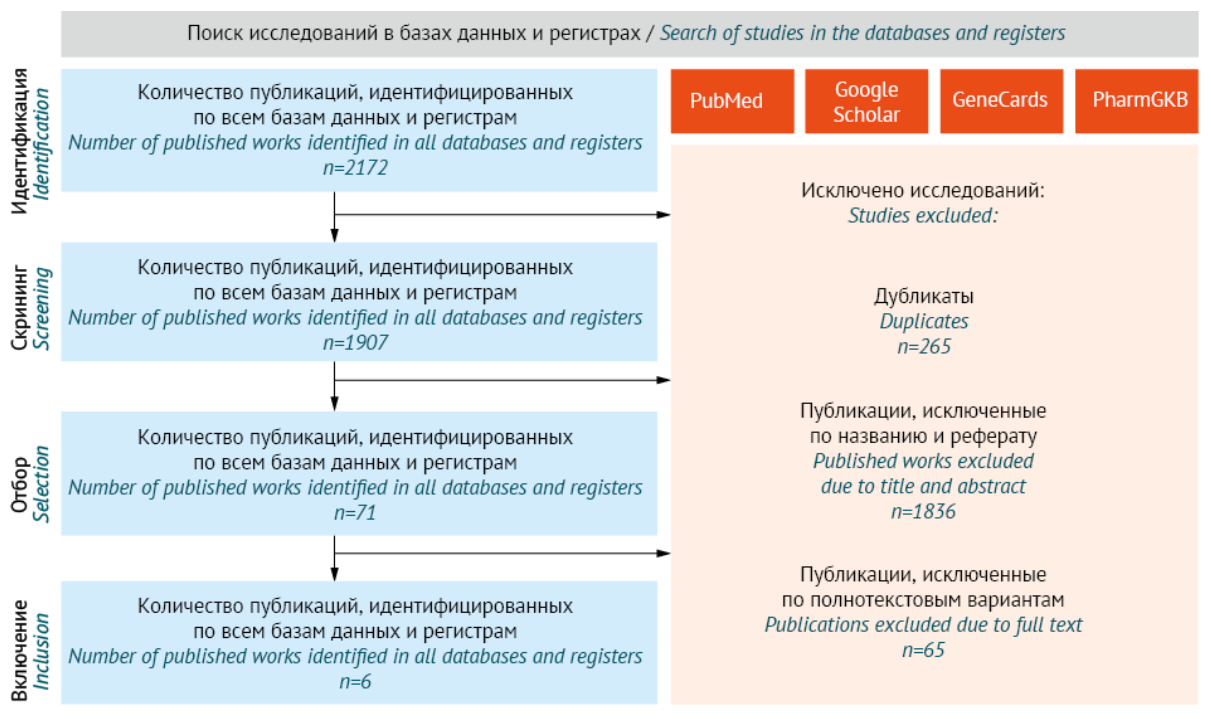
DISCUSSION. Research was conducted independently by two co-authors using PubMed, Google Scholar, GeneCads, and PharmGKB databases. A total of six (6) studies were selected that examined 17 candidate genes. The ADRA2A and DRD4 genes were associated with CIS. Polymorphism rs1800544 of ADRA2A gene regulates the expression of alpha-2A adrenoreceptor (ADRA2A). Alpha-2-adrenoreceptors regulate salivation, thus clozapine antagonistic effect causes CIS. Polymorphism of 120-bp DRD4 will reduce expression of type 4 dopamine receptor (DRD4). In turn, this may result in CIS as clozapine increases the receptor blockade. However, the results contradicted other studies, presumably due to assessment of different polymorphisms in the above studies. Moreover, the analysed studies had a number of methodological limitations.
CONCLUSIONS. The performed systematic review made it possible to identify CIS pharmacogenetic predictors. However, large multicenter studies using a strong prospective design and considering these limitations are required in order to develop a pharmacogenetic panel with high predictive accuracy for CIS.
REGISTRATION. This systematic review protocol is included in the national systematic review register (PROSPERO), Registry No. CRD420251089235.
INTRODUCTION. The first part of this article discussed antipsychotic-induced metabolic syndrome (AIMetS) as a common adverse reaction to the pharmacotherapy of psychiatric and addiction disorders. The authors presented a review of basic and additional clinical and biochemical biomarkers of metabolic syndrome (MetS) in general and AIMetS in particular in patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders and outlined approaches to measuring these biomarkers. Detecting changes in the expression of circulating microRNAs in the blood can be considered a promising method for predicting and diagnosing AIMetS.
AIM. This study aimed to evaluate the role of circulating microRNAs as epigenetic biomarkers of the key components of AIMetS pathogenesis.
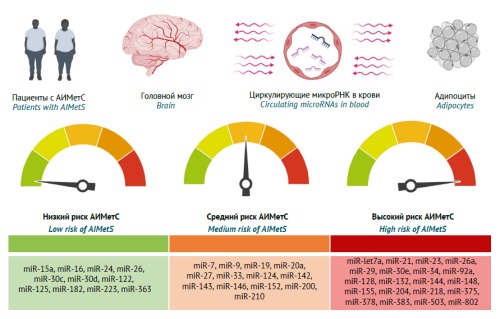
DISCUSSION. The authors reviewed and collated the results of academic and clinical research (2012–2024) with a focus on the role of circulating microRNAs involved in the key AIMetS pathogenesis and progression pathways. The authors analysed the results of studies on the role of circulating microRNAs in the blood as regulators of the key components of MetS and AIMetS pathogenesis. The studied components of pathogenesis included oxidative stress, systemic inflammation, adipogenesis regulation (and abdominal adiposity development), lipid metabolism, high- and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol homeostasis, atherogenesis, and hepatic steatosis, as well as the regulation of insulin and leptin sensitivity, glucose metabolism and appetite, and insulin, neuropeptide Y, orexin, thyroid and parathyroid hormone expression. A personalised assessment of the safety of pharmacotherapy may depend on the pattern of circulating microRNAs that induce or inhibit the main components of AIMetS pathogenesis. The differences in the results of the reviewed microRNA studies may be due to the differences in the design of these academic (mainly) and clinical studies and their lack of consideration for modifiable and unmodifiable risk factors for developing AIMetS. The authors proposed a microRNA classification according to the risk level of developing AIMetS.
CONCLUSIONS. The findings demonstrate that the sensitivity and specificity of epigenetic biomarkers of AIMetS can vary widely, depending on the nature of their influence (predictive or protective) on one or several pathogenetic components of this widespread adverse reaction to psychopharmacotherapy. The most studied microRNAs are predictive biomarkers of oxidative stress (miR-1, miR-21, miR-23b, miR-27a, etc.) and systemic inflammation (miR-21, miR-23a, miR-27a, etc.) in patients at high risk of developing MetS and AIMetS. Promising epigenetic AIMetS biomarkers include microRNAs that affect the expression of and sensitivity to neuropeptides, including neuropeptide Y (miR-let7b, miR-29b, miR-33, etc.), leptin (miR-let7a, miR-9, miR-30e, etc.), and orexin (miR-137, miR-637, miR-654, etc.).
PRECLINICAL STUDIES
INTRODUCTION. Ophthalmotoxicity assessment of potential drugs is a highly meaningful element of preclinical trials that reflects modes of action and pharmacological effects of a chemical compound on the eyes in topical and systemic use. However, there is no relevant common algorithm for ophthalmotoxicity assessment, suggesting expediency of summarising Russian and foreign experience.
AIM. This study aimed to develop an algorithm assessing ophthalmotoxicity of medicinal products in preclinical in vivo studies based on Russian and international guidelines.
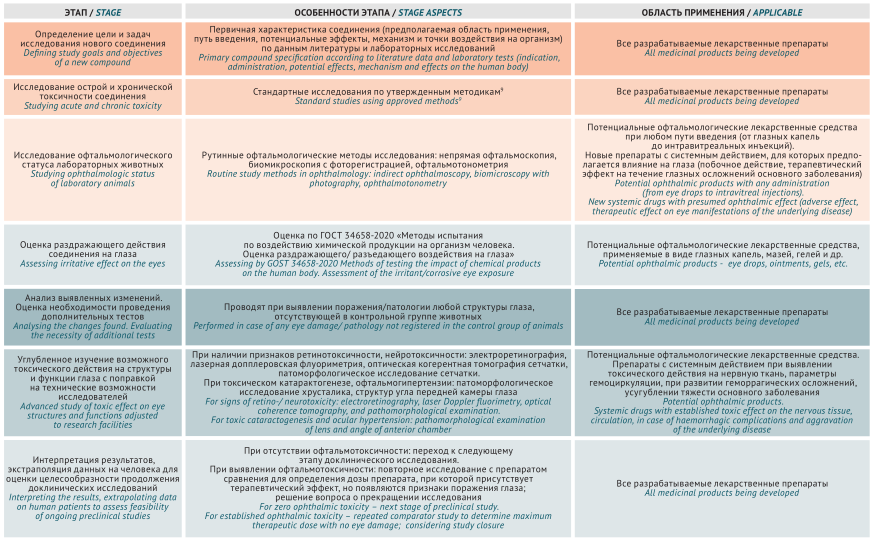
DISCUSSION. Study approaches of chemical compound ophthalmotoxicity were analysed in Russian and international regulatory documents (Guidelines for conducting preclinical studies of medicines, GOST 34658-2020, Guidelines of Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) No. 450 and No. 263). The recommended methods prove to be applicable in preclinical studies and make it possible to study the effect of chemical compounds on the structure (ophthalmoscopy, biomicroscopy, optical coherence tomography) and functions (electroretinography) of the eyes. The study included basic information on the comparative eye anatomy and physiology in mice, rats, and rabbits, crucial for studying irritant and retinotoxic effects and translating the results into clinical trials. Ophthalmotoxicity research methods and their practical application in typical laboratory animals were described in detail considering their anatomy and physiology. Based on generalised study data, a comprehensive differential approach is proposed for ophthalmotoxicity study of the developed medicinal products.
CONCLUSIONS. The proposed algorithm assessing ocular toxicity of ophthalmic and systemic drugs makes it possible to optimise the design and schedule of preclinical studies in animals and improve the safety of drug use in humans.
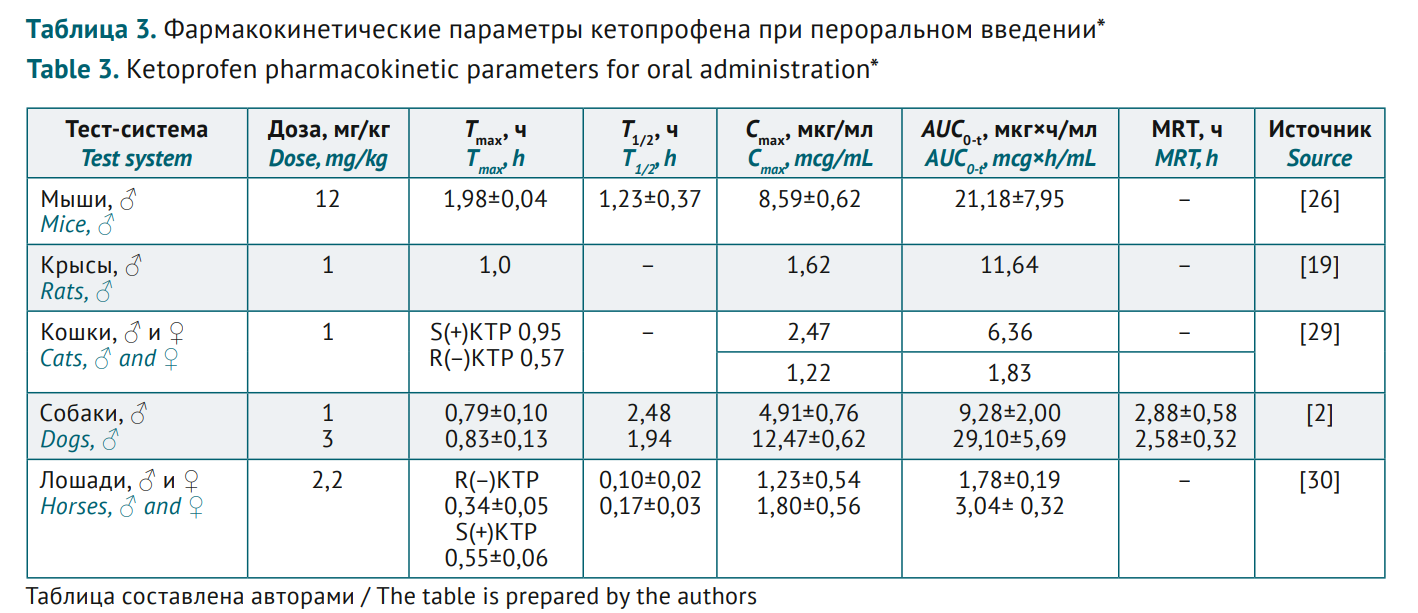
INTRODUCTION. Ketoprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with pronounced analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effect. Ketoprofen pharmacokinetics is comparatively well described in various in vivo models. Since it is potentially possible to create new dosage forms of ketoprofen, with pharmacokinetics studies contributing to high-quality pharmaceutical development, a comparative assessment is relevant for the data on animals and humans.
AIM. This study aimed to identify animal species relevant for preclinical studies of different ketoprofen dosage forms by summarising bioanalytical methods used to assess pharmacokinetics and by comparing various test systems.
DISCUSSION. Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet/mass spectrometric detection and acetonitrile or methanol-based eluents in various buffer solutions is the most ubiquitous method for ketoprofen analysis in biomaterials. Ketoprofen pharmacokinetics was studied in humans and animals of several phylogenetic species using various dosage forms (injectable solutions, tablets, paste forms, etc.) and the relevant administration (intravenous, intramuscular, oral, transdermal). High drug bioavailability was noted for different routes. Maximum concentration (Cmax) range at similar doses and similar time parameters (time to maximum concentration, Tmax, half-life, T1/2 and mean residence time, MRT) for the three main administration routes (oral, intravenous and intramuscular) was comparable in humans and rats, cats, and dogs; thus these test systems were suggested for pharmacokinetics studies of ketoprofen preparations.
CONCLUSIONS. The analysis suggested that rats and larger animals (cats, dogs) can serve as test systems in ketoprofen pharmacokinetics studies, at least for oral, intravenous, and intramuscular administration. Using ketoprofen as an example, the study showed feasibility of integrating heterogeneous pharmacokinetic data, as well as comparison challenges due to variable test systems, study objects, dosages, and administration routes.
INTRODUCTION. Mathematical models are actively used in biomedical research, including efficacy and safety prediction of medicinal products. Scientific Centre for Expert Evaluation of Medicinal Products has developed and implemented a method for preclinical benefit-risk assessment of medicinal products. The method is based on the binary classification of variables used to calculate WoE (Weight of Evidence) and IV (Information Value) predictors. Calculation algorithms for WoE and IV are based on Bayesian model of prior probability, which allows for risk prediction and informed decision-making regarding pharmacotherapy and its ability to reduce the genotoxic and embryotoxic effects of environmental teratogens. However, confirmed predictive ability warrants pharmacological validation of a potential corrector and the predictive system computation quality.
AIM. This study aimed to validate preclinical assessment method of the benefit-risk ratio by correcting reprotoxic effects of peat smoke in rats with pharmacotherapy as a case study.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. The study used experimental and statistical analysis. A method developed by Scientific Centre for Expert Evaluation of Medicinal Products was used to confirm predictive significance of preclinical benefit-risk assessment for pharmacotherapeutic correction of peat smoke-induced embryotoxic effects. In order to validate benefit-risk assessment mathematical model and the corrective pharmacological properties of fabomotizole in genotoxicity and embryotoxicity models induced by peat smoke in rats, logistic regression and ROC analysis methods were applied.
RESULTS. AUC analysis (0.701; 0.617–0.786) within pharmacological validation showed that fabomotizole corrective capacity in rats was predicted in the range from “unsatisfactory” to “good” (0.500; 0.239–0.761). This corresponds to WOE/IV estimates, from “low” to “moderate” weight (0.34; –0.99) and “weak” to “strong” information value (0.02; 0.45). Computation quality test for genotoxicity showed an AUC of 0.554 for the predicted probability and 0.432 for the predicted group (random guessing). For embryotoxicity, AUC was 0.701 and 0.782, indicating good predictive ability of the model.
CONCLUSIONS. The validation study has confirmed the predictive value of WoE and IV. The benefit-risk model based on Bayesian prior probability has shown high convergence with ROC analysis in assessing genotoxicity and embryotoxicity of peat smoke, as well as corrective capacity of fabomotizole.
CLINICAL STUDIES
INTRODUCTION. Valsartan+sacubitril (a combination of neprilysin inhibitor and angiotensin II receptor blocker) effectively reduces blood pressure (BP) and has the potential to improve metabolic parameters. However, despite this class of drugs being included in clinical guidelines, the specific indications in patients with arterial hypertension are not clearly defined, thus requiring a more detailed study.
AIM. This study aimed to assess valsartan+sacubitril combination used for treatment of arterial hypertension in adults in outpatient settings, specifically regarding its efficacy, safety, and impact on overall clinical outcomes and quality of life.
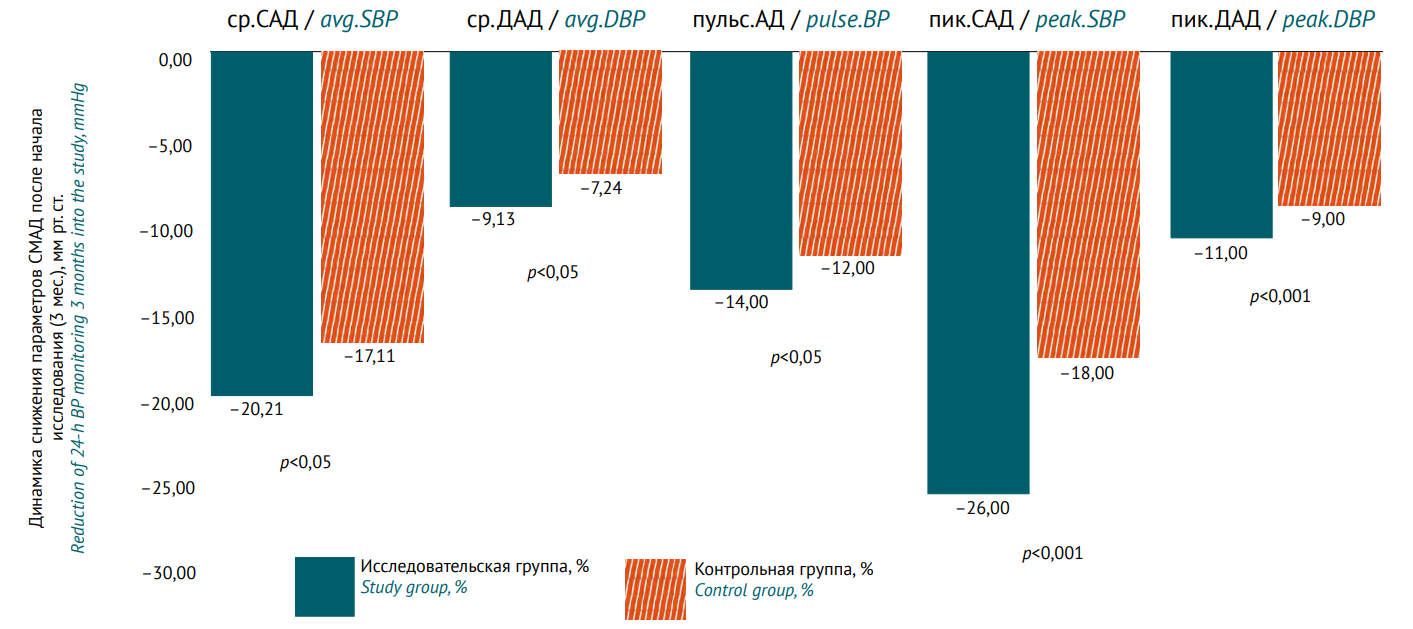
MATERIALS AND METHODS. The study is an open prospective longitudinal observation with active control. The study was conducted at State Autonomous Healthcare Institution “City Polyclinic No. 12” (city of Tyumen, Tyumen region). Patients were recruited from 01.10.2022 till 31.03.2025. For each patient, the observation period was 3 months for stage 1 (n=550) and 1 year for stage 2 (n=160). BP was controlled at the inclusion, at the end of stage 1, and after 3, 6, and 12 months of treatment. At stage 1, patients were divided into 4 groups: angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor (ACE) + diuretic (n=189), ACE inhibitor + calcium channel blocker (CCB) (n=121), angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) + diuretic (n=119), ARB + CCB (n=121). At stage 2, patients not achieving target BP ≤140/90 mmHg (n=160) were randomised into 2 groups: study group (n=80), patients receiving valsartan+sacubitril + diuretic/CCB; and control group (n=80), receiving a triple combination of ARB + diuretic + CCB or ACE inhibitor + diuretic + CCB.
RESULTS. At stage 2, the rate of patients achieving target BP was 93% in the study group vs. 83% in the control group after 3 months; 94% vs. 88% after 6 months; and 99% vs. 98% after 12 months, respectively. Average daily systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure after 3 months of treatment had a statistically significant difference in favour of the study group (p<0.05). Noteworthy is the positive effect on the reduction of peak average daily systolic, diastolic, as well as pulse BP, and blood pressure load (p<0.001). After 6 months, the difference between the groups remained the same for all the decreasing parameters (according to 24-h blood pressure monitoring). Only after 12 months did patients in the control group receive a comparable reduction in the parameters; no statistically significant differences were revealed (p>0.05). EQ-5D showed higher quality of life in the study group after 12 months, the average score being 0.82±0.08 vs. 0.69±0.10 in the control group (change +0.17 vs. +0.05; p<0.05). All adverse reactions for valsartan+sacubitril were predictable; the differences in the frequency of treatment discontinuation between the groups were not statistically significant.
CONCLUSIONS. Valsartan+sacubitril has demonstrated efficacy and safety in hypertension in adults. This combination can be recommended as a second-line treatment in case of ineffective two-component regimens of the first-line antihypertensive therapy.
INTRODUCTION. Despite its relatively low share in the structure of oncological incidence, cutaneous melanoma (CM) is one of the most cost-intensive nosologies. The emerging new combination treatment regimens require regular pharmacoeconomic monitoring.
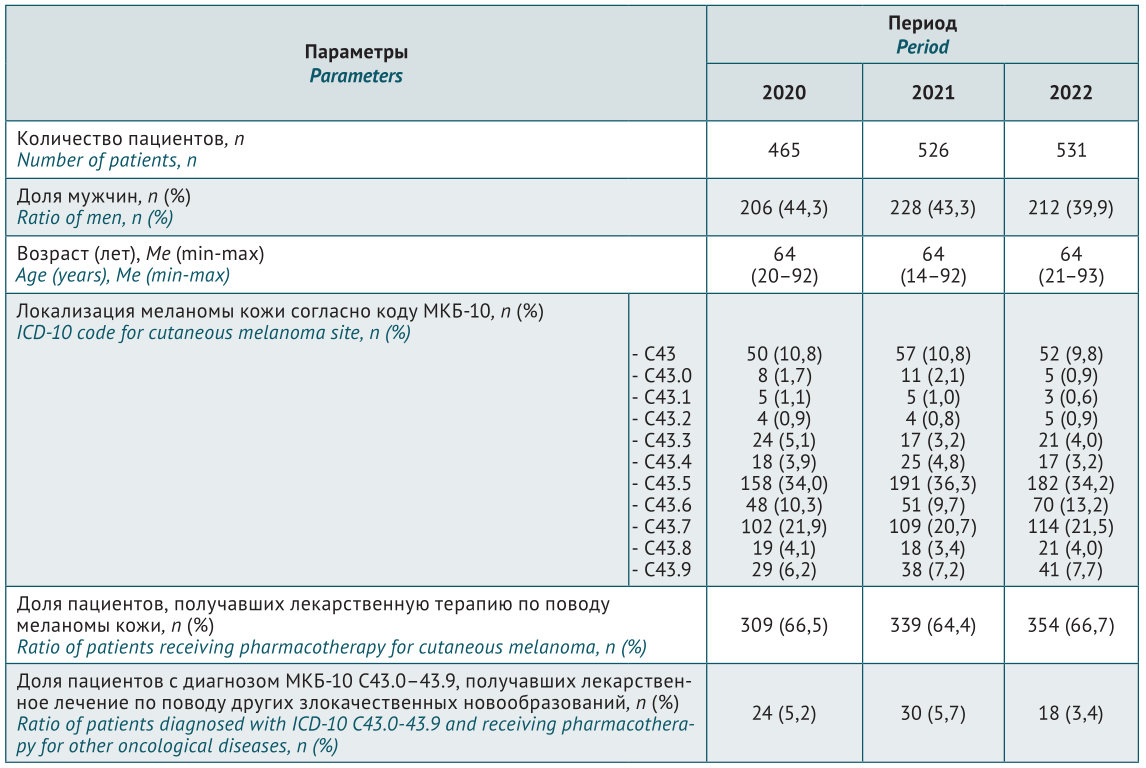
AIM. This study aimed to evaluate the current structure, dynamics, and costs of drug therapy in Moscow region over 2020–2022 based on pharmacoepidemiological and pharmacoeconomic analysis of subsidised drug provision in order to identify key regional trends.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Primary depersonalised data were obtained from patient medical records in the Unified Medical Information and Analytical System (EMIAS). The analysis included total number of patients and their clinical profile (gender, age, diagnosis code); for the drugs, international non-proprietary name, dosage form, dosage, number of packages sold, and total cost was analysed. Cost analysis considered both total cost and structure in terms of selected international non-proprietary names. An additional analysis was conducted for a three-year period.
RESULTS. Data from 1,522 patients diagnosed with ICD-10 C43.0–43.9 were examined (465 patients in 2020, 526 patients in 2021, and 531 patients in 2022). Over the study period, the number of patients increased by 14%, with gender structure gradually changing and the ratio of men decreasing from 44.3% to 39.9%. Two-thirds of the patients received drug therapy for the primary disease. Total outpatient costs ranged from 407.6 million rubles in 2020 to 615.3 million rubles in 2022. CM share of drug therapy averaged 98% of the total cost. Over 2020–2022, the highest patient coverage, number of packages, and cost level was attributed to dabrafenib+trametinib and vemurafenib+cobimetinib combinations. They accounted for an average of 85% of all patients and almost 99% of all costs. Over the 3-year period, there was a twofold cost increase for dabrafenib and trametinib, with a comparable twofold cost decrease for vemurafenib and cobimetinib.
CONCLUSIONS. Pharmacotherapy structure, dynamics, and cost has been evaluated in CM patients of Moscow region over 2020–2022. The obtained data can be used to optimise pharmacotherapy of CM patients at the regional level by widely introducing both clinical and pharmacoeconomic evaluation principles of treatment approaches.
ISSN 2619-1164 (Online)